What Process Would You Consider Essential for Maintaining Life?: Vital Insights

Cellular respiration and nutrient absorption are essential processes for maintaining life. Regular hydration and waste elimination also play critical roles.
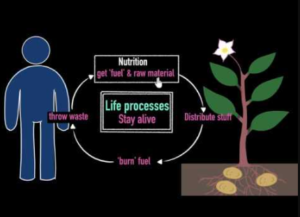
Maintaining life hinges on several vital processes that work in harmony. All living organisms require energy, which is primarily obtained through cellular respiration. This biological process enables cells to convert glucose and oxygen into energy, carbon dioxide, and water. Every living being also needs nutrients to build and repair tissues, which are absorbed from their diet.
Water is another critical component for metabolic processes and maintaining homeostasis. Proper hydration ensures that cells function optimally and the body remains balanced. Lastly, eliminating waste products is vital to avoid toxicity and maintain health. Together, these processes form the bedrock of life’s sustainability, allowing organisms to grow, reproduce, and thrive in their environments.
Contents
- 1 The Essence Of Life Processes
- 2 Breathing: The Inhale/exhale Cycle
- 3 Circulation: A Network Of Life
- 4 Nourishment: Fuel For The Cellular Engine
- 5 Hydration: The Element Of Life
- 6 Homeostasis: Keeping Balance In The Body
- 7 Sleep And Restoration: The Unseen Repair
- 8 Immune Defense: The Body’s Shield
- 9 Excretion: Purifying The System
- 10 Cellular Regeneration And Repair
- 11 Conclusion
The Essence Of Life Processes
Exploring the inner workings of living organisms unveils a complex web of functions. These functions are critical to survival. They ensure growth, repair, and continuation of life. Each biological process plays a fundamental role in the lively dance of existence. This post sheds light on what keeps us ticking every second of our lives.
Defining Life’s Core Functions
What functions are non-negotiable for life? At the heart are cellular processes. They convert nutrients into energy, drive growth, and repair tissues. We also need waste removal systems. They keep cells clean for optimal performance. Respiration, nourishment, and waste elimination are pillars of maintaining life.
- Cellular Respiration: Cells get energy from oxygen and glucose.
- Nutrient Uptake: Digestive systems break down food into usable forms.
- Waste Removal: Toxins and waste exit the body through diverse pathways.
Interconnectedness Of Vital Processes
No life process stands alone. They link in a chain of survival. For instance:
| Process | Connection |
| Circulation | Transports nutrients and oxygen to cells. |
| Respiration | It uses oxygen to release energy from food. |
| Excretion | Eliminates metabolic waste. |
Each system relies on the other to function. They work as a team, not in isolation. The body balances these activities efficiently. This constant balancing act is homeostasis. It keeps our internal environment stable.
Breathing: The Inhale/exhale Cycle
Let’s dive deeply into breathing: The inhale/exhale cycle. This cycle is like a round-the-clock engine keeping us alive. We’ll explore how this simple yet vital process fuels every cell in our bodies.
Oxygen Intake And Carbon Dioxide Excretion
Breathing in pulls oxygen into our lungs. This oxygen travels through our blood to all our organs and tissues. Breathing out eliminates carbon dioxide, a waste gas our bodies don’t need.
- Oxygen enters the bloodstream and reaches every part of the body.
- Cells use oxygen to make energy from the food we eat.
- Carbon dioxide, produced in this process, travels back to the lungs.
- We exhale carbon dioxide and keep the cycle going.
Respiratory System’s Role In Life Maintenance
The respiratory system is like a complex factory. Its main job is to keep the oxygen coming in and the carbon dioxide going out. The system includes your nose, throat, windpipe, and lungs.
| Part | Function |
| Nose | Filters and warms the air |
| Throat & Windpipe | Carries air to lungs |
| Lungs | Air sacs exchange gases |
The entire system works together so you can inhale oxygen and exhale carbon dioxide.
Circulation: A Network Of Life
Think of a busy city with cars and buses moving around. Now, imagine our body as a big city. The roads are blood vessels. The cars and buses are blood. This is what we call circulation. It keeps us alive. It brings food to our cells. It takes away the trash. Let us dive into the essential process that powers our life.
Heart’s Pumping Mechanism
The heart is the boss of circulation. It works like a pump. Think of squeezing a water bottle. Water squirts out. That’s what the heart does with blood. Every squeeze sends blood on a trip around the body.
- Right Side: Sends blood to the lungs to pick up oxygen.
- Left Side: Pumps the blood rich with oxygen to the body.
Transportation Of Nutrients And Waste
Our blood has a super important job. Think of it as a delivery van. It carries food to every house (cell) in the city (body). Blood also picks up garbage (waste) from the houses. It’s a two-way street.
| What Blood Carries | Where It Goes |
| Oxygen | To Cells |
| Nutrients | To Cells |
| Carbon Dioxide | To Lungs |
| Waste Products | To Kidneys |
Nourishment: Fuel For The Cellular Engine
Imagine each cell in your body as a tiny engine. Just like a car needs fuel, your cells need nourishment. Without proper food, these cellular engines can’t function. This is why eating isn’t just enjoyable; it’s essential. Yet, it’s not just any food that keeps us running; it’s the right food, digested and assimilated perfectly, that powers the intricate systems within us.
Digestion And Assimilation Of Food
Digestion kicks off this essential process. It breaks down food into nutrients. Assimilation then takes these nutrients into the bloodstream. Here, they travel to where they’re most needed. Let’s break down this journey:
- Starts in the mouth: Enzymes in saliva begin digestion.
- Moves to the stomach: Acid and enzymes continue the process.
- Small intestine gets to work: Here, most nutrients are absorbed.
- Finally, the bloodstream distributes these nutrients through the body.
This process ensures each cell gets the right fuel to thrive and maintain life.
Balanced Diet’s Importance
Balance in your diet is like balance in life—crucial. Each food group plays a different role:
| Food Group | Role |
| Proteins | Build and repair tissues |
| Carbohydrates | Provide energy |
| Fats | Support cellular growth |
| Vitamins & Minerals | Boost immune system and other functions |
| Water | Hydrate and assist in various bodily functions |
Eating from each group ensures your cells get diverse and rich resources. A balanced diet supports every part of your body. It helps the heartbeat, the lungs breathe, and the muscles move. Your body functions smoothly when your diet aligns with your body’s needs.
Hydration: The Element Of Life
Water is not just a drink; it is the cornerstone of life. Every cell needs water to function correctly, so we must hydrate regularly to live healthily.
Water’s Function In Biological Systems
Water serves as the lifeblood of our cells. It plays a part in:
- Transporting nutrients and oxygen.
- Removing waste products from the body.
- Regulating body temperature through sweating.
- Acting as a lubricant for joints and tissues.
- Enabling chemical reactions in the body.
Impact Of Hydration On Physical Well-being
Staying hydrated means more energy and better performance. Benefits of proper hydration include:
| Benefit | Description |
| Enhanced Endurance | Water keeps muscles energized. Less water, less muscle power. |
| Improved Focus | The brain is 75% water. Good hydration keeps it sharp. |
| Better Detoxification | Water flushes out toxins through the kidneys. |
| Healthier Skin | Hydration keeps skin supple and reduces wrinkles. |
Remember, dehydration affects the body’s ability to function. Signs of dehydration include:
- Dry mouth and thirst.
- Headaches and dizziness.
- Fatigue and irritability.
- Dry skin and eyes.
Drink water throughout the day to keep these symptoms at bay. Your body and mind will thank you.
Homeostasis: Keeping Balance In The Body
A homeostasis is a balancing act essential for life. Our bodies always work to stay stable. This balance lets cells live, grow, and keep us healthy. The body’s conditions, like temperature and pH, must stay right. This happens no matter what is going on outside.
Regulation Of Internal Conditions
Our bodies have intelligent ways to keep balance. Think of it as the body’s AC and heating system. Temperature, blood sugar, and water levels must stay in check.
- Sensors in the body notice changes.
- Messages go to the brain saying, “Something’s off!”
- The brain sends signals to organs to fix the problem.
This works like a thermostat. When it gets too hot or cold, sensors tell the heater or AC to turn on or off.
Homeostatic Imbalances And Diseases
When the balance is off, we may get sick. Diseases can happen if the body’s system can’t fix an imbalance. Diabetes, for example, is when blood sugar levels are too high or too low.
| Disease | Imbalance | Body’s Response |
| Diabetes | Blood sugar too high/low | Insulin management issues |
| Hypertension | Blood pressure high | Vessel constriction |
Catching these imbalances early helps us stay healthy. Regular check-ups and tests can find problems before they get big.
Sleep And Restoration: The Unseen Repair
What supports a healthy life? Good food, water, air, exercise, and sleep. This last piece, sleep, is vital to our health and daily repair. Much happens when we sleep. Our bodies fix themselves. Our brains sort memories. Without sleep, we can’t function at our best. This part of the blog dives into sleep’s role in health and recovery and the risky territory of sleep deprivation.
Role Of Sleep In Health And Recovery
Sleep does wonders for the body and mind. It’s crucial for physical and mental health. What happens during sleep?
- Muscles repair themselves
- Hormones balance out
- The brain clears out waste
- Memory gets stronger
- Immune system gears up for defense
Think of sleeping as plugging in your phone. It recharges you. Good sleep can make you feel alert and ready for the day. It also helps in fighting illnesses. Chronic sleep issues can lead to health problems.
| Sleep Benefits Table | |
| Benefit | Description |
| Memory Improvement | Sleep consolidates memories, making learning more accessible. |
| Healing Boost | The body repairs tissue and cells faster while you sleep. |
| Stress Reduction | Quality sleep reduces stress, improving overall well-being. |
Consequences Of Sleep Deprivation
Skip sleep, and you’ll feel it. Your body and mood can both drop. Here is what might happen if you don’t sleep enough:
- Irritability and mood swings
- Focus and memory suffer
- The risk of illnesses raises
- Weight can increase
- Healing slows down
Long-term sleep loss can lead to chronic conditions, heart health issues, and blood sugar issues. So, tucking in for enough hours is critical. Don’t let sleep slide. It’s a pillar of health, just like diet and exercise.
Immune Defense: The Body’s Shield
Just like knights had shields for protection, our bodies have the immune system. This shield guards us against invaders called germs. Without it, these germs could make us very sick. But with a robust immune system, we can stay fit and healthy. Let’s explore how this notable shield works.
Pathogen Recognition And Response
Our body knows how to spot enemies. When germs invade, it quickly figures out they don’t belong. The immune system then sends notable fighters to tackle them.
Cells called ‘white blood cells’ lead the charge. They find and destroy germs to keep us healthy. Here’s how they do it:
- Scout cells find the germs.
- Soldier cells fight the germs.
- Memory cells remember the germs for next time.
This team works together to ensure germs don’t stand a chance. They learn and adapt, becoming more robust with each battle.
Maintaining Immune Health
A robust immune system is vital. Like a sports team, it needs good care to perform well. Here’s what helps:
- Eat plenty of fruits and vegetables – Like the body’s training food.
- Stay active – Exercise makes the immune system robust.
- Get enough sleep – It’s like a rest period for your immune fighters.
- Stay away from germs – Wash hands often and sneeze into your elbow.
By taking these steps, your immune defence stays ready for anything. It’s a shield that’s always there, keeping you safe and sound.
Excretion: Purifying The System
Our bodies are like busy factories, constantly working to keep us healthy. Just as factories have waste products that need disposal, our bodies also create waste. This waste, if not removed, can harm us. That’s where excretion comes in. Excretion is a vital process that cleans our system. It helps us stay healthy by getting rid of waste. Now, let’s dive into how excretion works and its importance.
Eliminating Metabolic Waste
Metabolic waste is what our cells leave behind after using the energy from our food. Think of it as leftover packaging from a snack. Our bodies must throw this waste out, or we can get sick. How do we do this? Here are a few ways:
- Lungs: We breathe out carbon dioxide, a waste gas our cells make.
- Kidneys: They filter out waste from our blood and make urine.
- Skin: When we sweat, we remove excess salt and even a little urea, another waste product.
Detoxification Organs And Their Functions
Our body has particular organs that work hard to detoxify. Let’s meet these cleaners:
| Organ | Function |
| Liver | Transforms toxins into safer substances that we can remove. |
| Kidneys | Filter out toxins from our blood before they can harm us. |
| Colon | Pushes digestive waste out of the body through bowel movements. |
| Skin | It uses sweat to remove waste and control body temperature. |
Cellular Regeneration And Repair
Our bodies are remarkable, continually mending and renewing to keep us flourishing. This lifelong dance of destruction and creation is foundational for health.
Imagine cells as tiny heroes in a vast universe within us, always ready to repair damages or replace fallen comrades. Without this fabulous process, life would fail to prosper.
Tissue Renewal And The Healing Process
Is your skin grazed or muscle torn? Don’t worry! Tissue renewal enters the stage, where damaged cells bow out, making room for new actors in the play of healing.
Our bodies curate this process with finesse, using cellular signals like cues in a grand performance.
- Skin cells replenish – a critical shield reformed.
- Blood cells regenerate – life’s elixir flows anew.
- Muscle repair – strength and movement restored.
Stem Cells And Regenerative Medicine
Stem cells, the chameleons of the cellular world, hold the potential to morph into any cell type needed, spearheading the future of healing. They are the quiet architects of regeneration.
Regenerative medicine harnesses this power to heal symptoms and the root cause of illness.
| Stem Cell Type | Potential | Application |
| Embryonic Stem Cells | It can become any cell | Treating diverse diseases |
| Adult Stem Cells | More specialized | Targeted therapies |
| Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells | Flexible and versatile | Personalized medicine |
Conclusion
As we’ve explored, sustaining life hinges on a delicate ballet of processes. Proper hydration, balanced nutrition, consistent exercise, and adequate sleep are non-negotiable. These pillars form the foundation for ongoing health and vitality. Honouring them fuels our journey through life’s twists and turns.